.png)
Atomic Structure Lesson 1
⚛️ Lesson 1 ⚛️
Get Ready by joining Lesson 1 , it is easy but you need to know it .Explore the structure of an atom and its subatomic particles in this visually enhanced quiz. Learn about atomic and ionic radii, understand the role of protons, neutrons, and electrons, and discover how to determine the number of neutrons in an atom. Embark on a journey through the microcosm of atoms and ions and unlock the secrets of the periodic table!
⚛️ 1.1.1Structure of an Atom ⚛️
Welcome ! Today we are diving into the heart of matter to understand the structure of an atom. Let's get started!
💠 Atomic Structure 💠
Matter, as we know it, is composed of atoms, the smallest particles of an element capable of engaging in chemical reactions. The core of an atom is a very small, dense nucleus surrounded by a large area of mostly empty space.
1️⃣ Nucleus: It contains protons and neutrons, giving the nucleus an overall positive charge.
2️⃣ Protons: These particles carry a positive charge.
3️⃣ Neutrons: These particles are neutral, with no charge.
4️⃣ Electrons: These are negatively charged particles that reside in orbitals around the nucleus.
Remember, the diagram of an atom is not to scale; the nucleus is much smaller compared to the overall size of the atom.
🎲 Subatomic Particles 🎲
Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons, referred to as subatomic particles. Their masses and charges are usually relative and not actual charges and masses.
1️⃣ Protons and Neutrons: They both have a similar mass and are assigned a relative mass of 1.
2️⃣ Electrons: They are 1836 times smaller than a proton or a neutron, and their mass is usually considered negligible.
Here are their relative masses and charges:
Proton: Relative mass = 1, Charge = +1
Neutron: Relative mass = 1, Charge = 0
Electron: Relative mass ≈ 0 (negligible), Charge = -1
Q1: What are the relative masses and charges of protons, neutrons, and electrons?
🐘🪶 Picture this: a colossal elephant 🐘 named Proton, a mighty rhino 🦏 named Neutron, and a tiny, agile mouse 🐁 called Electron. These three are the heart and soul of our extraordinary, molecular circus, much like protons, neutrons, and electrons being the star ⭐ performers in the grand show of an atom.
Just like in a regular circus, it's important to know our performers' talents and traits. But we can't use the conventional tools 🔧🔨! Imagine trying to weigh these performers on a feather 🪶 scale. It's just not accurate enough! It's the same with subatomic particles: we can't measure their masses and charges using everyday units like grams or coulombs.
So, to bypass this problem, we dive into the world of 'relatives' 🎭.
Imagine if we said, "Compared to the elephant 🐘, the rhino 🦏 weighs the same, but the mouse 🐁 is much, much lighter." We're not giving their weights in pounds or kilograms; instead, we're comparing their weights relative to each other.
In the same manner, the mass of a proton is taken as a standard 🏆 (like our elephant 🐘), and it's given a 'relative mass' of 1️⃣. The neutron (our rhino 🦏) also weighs as much as the proton, so it too has a relative mass of 1️⃣. But our tiny mouse 🐁, the electron, is much lighter, with a relative mass of only 1/1836 ❗
And just like our performers have different weights, they also have different charges. The proton (our jolly, positive 🟢 elephant) has a relative charge of +1️⃣, the electron (the negatively charged 🔴 mouse) has -1️⃣, and the neutron (the neutral 🔘 rhino) is a 0️⃣.
So remember, these 'relative' masses and charges are like comparisons, not actual masses or charges.
It's like comparing our elephant, rhino, and mouse in our molecular circus! 🎪🌈
🔑 Atomic Key Terms 🔑
There are a few terms that you need to know to understand the structure of an atom.
1️⃣ Atomic Number (Z): It is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. In a neutral atom, the atomic number is also equal to the number of electrons.
2️⃣ Mass Number (A): It is the total number of protons and neutrons (nucleons) in the nucleus of an atom.
The number of neutrons in an atom can be calculated by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number.
Number of Neutrons = Mass Number - Atomic Number
Q2: If an atom has a mass number of 11 and an atomic number of 5, how many neutrons does it have?
📚 Exam Tip 📚
In the Periodic Table, each element is represented with its mass number and atomic number. This notation helps us understand the structure of the atom for that particular element.
Stay tuned for more lessons where we delve deeper into the Periodic Table and explore the properties and behaviors of atoms! 💥🔬📚 Quiz Level 1: Beginner Level 🌱
What is the smallest part of an element that can participate in chemical reactions? 🤔
Where are protons and neutrons found in an atom? 📍
What is the charge of an electron? ⚡
What do we call the particles that an atom is made up of? 🎭
What is the relative mass of an electron compared to protons and neutrons? ⚖️
Answers:
An atom.
In the nucleus of an atom.
Negative.
Subatomic particles.
The mass of an electron is often considered negligible, being around 1/1836 times smaller than that of protons and neutrons.
Level 2: Novice Explorer 🧭 Quiz
What are the charges of protons, neutrons, and electrons, respectively? 🌈
What does the atomic number of an atom tell us? 🔢
What is the term for protons and neutrons together? 🤝
How can we calculate the number of neutrons in an atom? 🧮
What is the space called that electrons move around in, outside the nucleus? 🌌
Answers:
Protons have a positive charge, neutrons have no charge (neutral), and electrons have a negative charge.
The atomic number tells us the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
Protons and neutrons together are called nucleons.
The number of neutrons = mass number - atomic number.
This space is called the electron cloud or orbitals. ⚛️ Level 3 Questions: Structure of an Atom ⚛️: Practicing More 💪
🔬💫 Level 3: Structure of an Atom 💫🔬
Describe the structure of an atom, giving details of the subatomic particles present. [6]
Explain the terms atomic number and nucleon number. [2]
💡 Atomic Number (Z) - The atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, determining its unique identity. 🎯
💡 Nucleon Number (A) - The nucleon number, also known as the mass number, signifies the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. 🔢
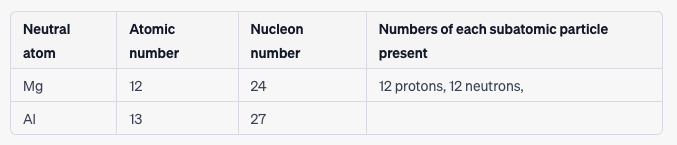
Copy and complete the table: 📋
[2]
Explain why atoms are neutral. [1]
An oxygen atom has 8 protons in its nucleus. Explain why it cannot have 9 protons. [1]
When calculating the relative mass of an atom, the electrons are not used in the calculation. Explain why not. [1]
🌟💡 Level 3 Answers: Structure of an Atom 💡🌟
The structure of an atom revolves around its nucleus, containing protons and neutrons, while electrons occupy energy levels or shells surrounding the nucleus. Protons bear a positive charge, neutrons are neutral, and electrons carry a negative charge. ⚛️
Atomic Number (Z) signifies the count of protons, determining the element's identity. It corresponds to the number of electrons in a neutral atom. 💫
Nucleon Number (A) accounts for the total protons and neutrons present in the nucleus, representing the atom's mass. 📊
Atoms are neutral since they possess an equal number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons. This balance of charges yields an overall neutral charge. ⚖️
An oxygen atom with 8 protons cannot have 9 protons since the number of protons defines its identity as oxygen. Altering the proton count would result in a different element. 🚫
When calculating the relative mass of an atom, electrons are not considered due to their significantly smaller mass compared to protons and neutrons. An electron's mass is approximately 1/1836 amu, whereas protons and neutrons have a mass close to 1 amu. Consequently, electrons have a negligible impact on the overall mass calculation. ⚖️❌
Stay tuned for more exciting lessons on the atomic world and its mesmerizing phenomena! 🌌🔬✨
Quiz Level 4: Pro Player 🏅
If an atom's mass number is 12 and its atomic number is 6, how many neutrons does it have? 🧠
Why is an atom mainly empty space? 🌌
Can the number of protons in an atom change? Why or why not? 🔄
What is the role of electrons in chemical reactions? ⚗️
If an atom gains an electron, does it become positively or negatively charged? Why? 🎭 Answers:
The atom has 6 neutrons (mass number - atomic number = 12 - 6).
An atom is mainly empty space because the electrons orbit the nucleus in this space, and electrons are much smaller than the nucleus.
The number of protons in an atom cannot change, as changing the number of protons would change the identity of the element (its atomic number).
Electrons participate in chemical bonds, either being transferred (ionic bonds) or shared (covalent bonds) between atoms.
If an atom gains an electron, it becomes negatively charged because electrons carry a negative charge.
Quiz Level 5: Expert Challenger 🏆
What determines the identity of an element? 🔎
How does the arrangement of electrons impact the chemical properties of an atom? 🌈
How does the atomic number affect the position of an element in the periodic table? 📚
What happens to the charge of an atom if it loses an electron? Why? 🎭
If an atom's mass number is 14 and it has 7 neutrons, what is its atomic number? 🧮
Answers:
The number of protons (atomic number) in an atom determines the identity of an element.
The arrangement of electrons, especially those in the outermost shell (valence electrons), impacts the chemical properties of an atom as they are involved in bonding.
The atomic number determines the position of an element in the periodic table; elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
If an atom loses an electron, it becomes positively charged because it loses a negatively charged particle.
The atom has an atomic number of 7 (mass number - number of neutrons = 14 - 7).